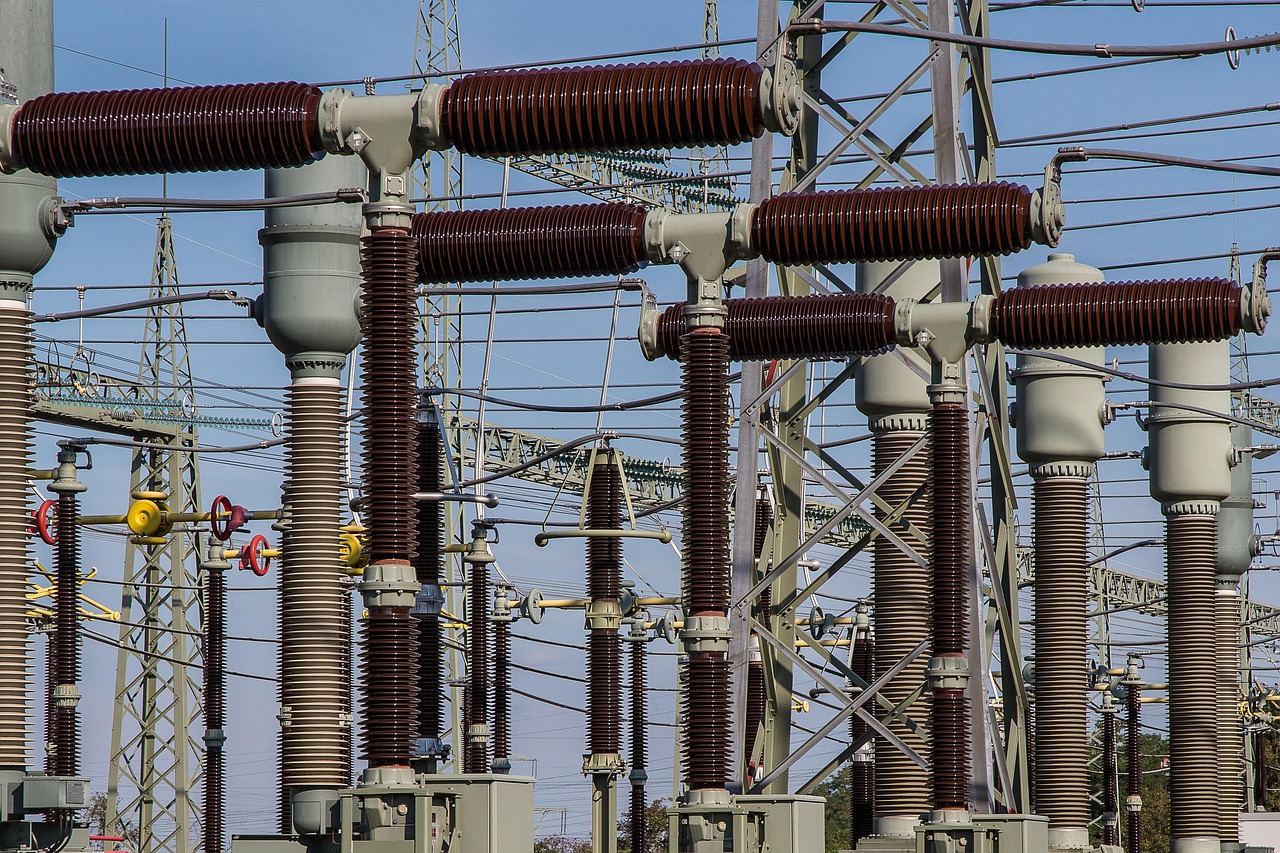
As Brazil continues to lead in the deployment of 500kV and 765kV+ ultra-high voltage (UHV) corridors, the transition toward autonomous inspection has become a strategic necessity. While this evolution drives operational efficiency, the unique electromagnetic landscape of Brazil’s grid introduces a critical hurdle: Electromagnetic Interference (EMI). For local Grid Operations Managers, addressing these environmental stresses through specialized power systems is essential for securing mission continuity and long-term asset reliability.
Key Takeaways
Identify the specific sources of electromagnetic stress in 500kV+ environments to prevent sensor drift and navigation errors.
Prioritize integrated shielding strategies to maintain telemetry integrity and flight stability during autonomous missions.
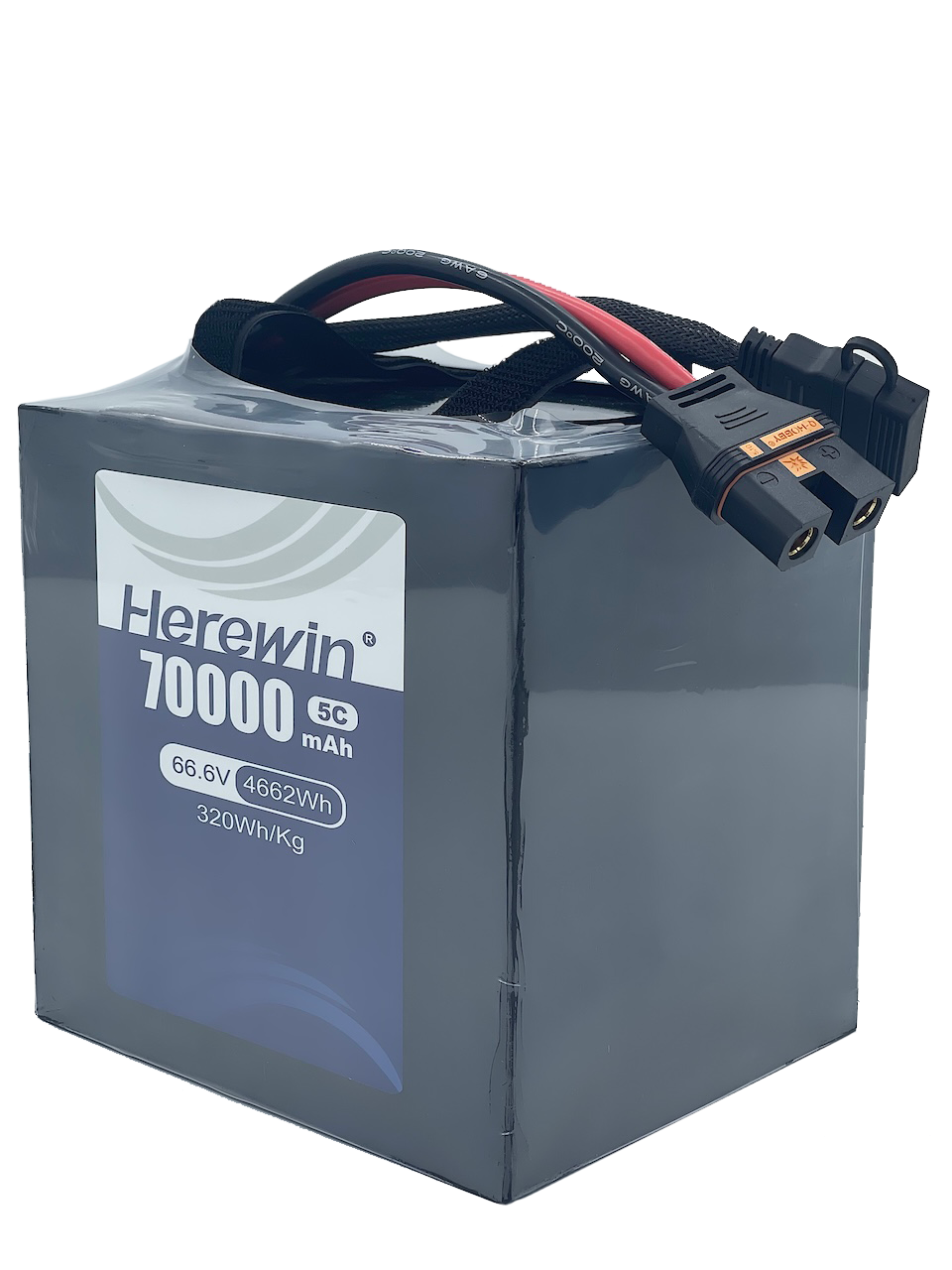
Utilize intelligent Battery Management Systems (BMS) capable of real-time health tracking and interference-resistant data feedback.
Shift toward semi-solid state chemistry (300–400 Wh/kg) to enhance thermal stability and achieve a 1,000–3,000 cycle service life.
Adopt a comprehensive safety architecture to streamline fleet integration and ensure compliance with industrial reliability standards.
Understanding EMI Challenges in Grid Settings

Identifying Sources of Electromagnetic Stress
In ultra-high voltage (UHV) environments, drones are exposed to intense electromagnetic interference (EMI) that can compromise mission integrity. Key sources of stress include:
Transmission Lines: 500kV and 765kV+ lines emit powerful electromagnetic fields that disrupt sensitive onboard sensors.
Substation Infrastructure: Transformers and switchgear generate localized EMI spikes, especially during switching operations or load fluctuations.
Environmental Synergies: Extreme temperatures and high winds increase motor loads, making battery systems more susceptible to EMI-induced performance drops.
Impact Analysis on Flight Stability
EMI creates cascading risks for autonomous drone operations. When a power system lacks sufficient industrial shielding, the following failures often occur:
Telemetry Corruption: Interference disrupts GPS and navigation signals, leading to positioning drift that is catastrophic in proximity to energized lines.
BMS Signal Noise: EMI can cause standard Battery Management Systems to report erroneous State-of-Charge (SoC) or temperature data, triggering false safety protocols.
Thermal and Mechanical Stress: High-voltage fields can contribute to induced heat, which, in liquid-electrolyte batteries, increases the risk of cell swelling or mechanical failure.
Understanding these complex sources is the first step toward mitigating their effects on your drone inspections. To ensure successful High-Voltage Autonomous Inspection, you must implement effective shielding and mitigation strategies against EMI. Taking this proactive approach will not only enhance flight stability but also protect your critical assets and ensure the continuity of your operations.
The Importance of Power System Integrity for Autonomous Inspection
In the realm of High-Voltage Autonomous Inspection, ensuring power system integrity is a critical safeguard for mission success. As drones navigate 500kV+ environments, the surge in electromagnetic interference (EMI) can compromise flight control and telemetry precision. Implementing a dual-layer defense—combining physical battery resilience with advanced digital signal filtering—acts as an essential barrier, allowing for smooth operation and sustained flight stability even in high-stress zones.
Signal Integrity & System Stability
An integrated Smart BMS serves as a proactive defense layer by ensuring Signal Integrity and system-wide stability. This architecture is designed to maintain high-fidelity performance through:
Adaptive Signal Filtering: The BMS actively filters electrical interference during real-time monitoring, ensuring that environmental electromagnetic stress does not trigger false safety protocols.
Stable Current Delivery: By providing a consistent discharge curve, the system minimizes voltage ripples that can compromise sensor accuracy during autonomous navigation.
Proactive Health Monitoring: Utilizing high-precision sampling, the system detects health anomalies (SoH) early, serving as an early-warning buffer against unpredictable interference.
By utilizing an integrated Smart BMS, you can effectively maintain operational stability, establishing a foundation of reliability for High-Voltage Autonomous Inspection missions.
Data Integrity for Regulatory Compliance
In the high-stakes world of grid operations, maintaining data integrity is a baseline requirement for meeting international safety and operational standards. A resilient power architecture ensures that the telemetry collected during 500kV+ inspections remains accurate, verifiable, and free from electromagnetic distortion.
High-Fidelity Data Collection: By providing a stable discharge curve and minimizing voltage ripples, the power system ensures that onboard sensors receive a consistent current, enabling the high-precision data capture required for critical infrastructure assessments.
Smart Maintenance & Pre-warning: Leveraging an integrated Smart BMS to track real-time State-of-Health (SoH) allows operators to detect anomalies before they escalate. This ensures every mission is supported by a reliable performance record, aligning with the rigorous standards of grid asset management.
Audit-Ready Reporting: Reliable energy output prevents “silent failures” or signal noise in sensor logs. This allows technical leads to generate high-fidelity reports for stakeholders, demonstrating a measurable commitment to safety and industrial excellence.
By prioritizing data integrity within your power system, you ensure that every autonomous flight contributes to a reliable, audit-ready history of your grid assets.
Overcoming Operational Barriers with Semi-Solid State Innovation
Beyond signal integrity, the primary challenge in UHV corridors is maintaining mission safety under extreme thermal and mechanical stress. While traditional liquid batteries face higher risks of degradation and thermal runaway, semi-solid state technology introduces a fundamentally more resilient energy architecture.
Thermal Stability Against Induced Heat
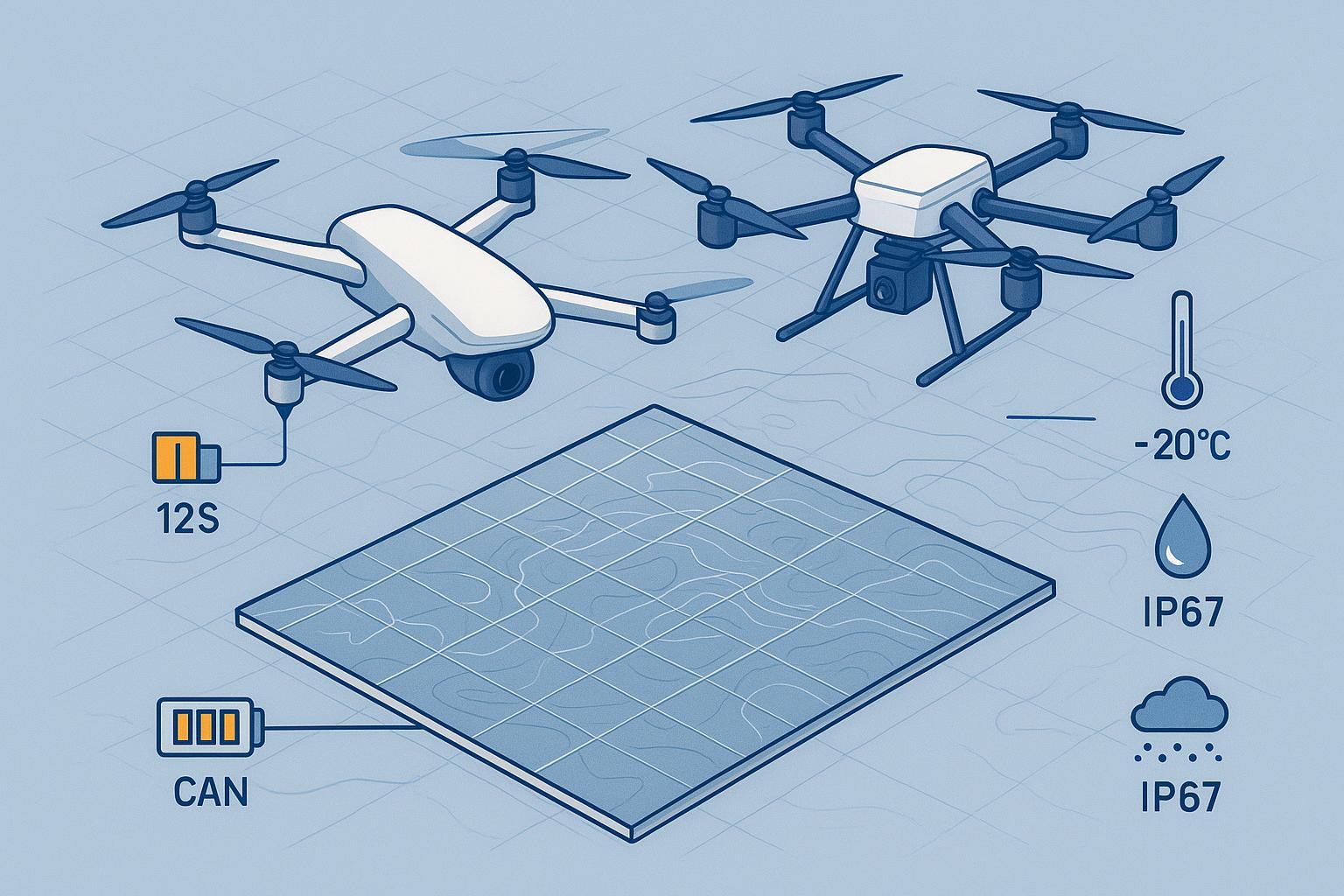
Semi-solid state batteries offer superior thermal stability by utilizing a specialized electrolyte system where liquid content is reduced to 5%-10%.
Advanced Heat Resistance: These batteries exhibit a temperature rise rate 60% lower than traditional lithium batteries during extreme stress scenarios.
Minimized Thermal Runaway Risk: By using a gel-like electrolyte, the system significantly minimizes the risk of leakage and thermal runaway, even during high-power maneuvers.
Consistent Performance: The chemistry remains robust across diverse climates, maintaining a capacity retention rate of ≥80% at temperatures as low as -20°C.
The implementation of semi-solid chemistry establishes a structurally safer energy foundation, inherently suited to withstand the unique thermal demands of high-voltage corridor operations.
Degradation Resilience and TCO Optimization
Scaling an autonomous fleet requires balancing peak performance with long-term economic viability.
Extended Mission Capability: By achieving energy densities of 300–400 Wh/kg, this technology significantly extends the flight endurance required for comprehensive grid inspections.
Ultra-Long Cycle Life: These systems are engineered to endure 1,000 to 3,000 charge cycles while maintaining over 80% of their capacity.
Optimized TCO: Higher energy density and longer lifespans directly reduce replacement frequency and long-term maintenance costs.
A unified management framework is essential to capitalize on these technical gains and ensure consistent performance across large-scale operations.
Scaling Your Fleet with the 6S Safety Architecture
Standardizing Operations via the Herewin 6S Framework
To achieve operational excellence in high-voltage drone inspections, a structured approach is required to transform high-performance hardware into a reliable fleet. The 6S Framework provides a comprehensive methodology for standardizing operations across six key pillars:
Safety: Prioritize thermal stability with semi-solid chemistry to mitigate heat-related risks, protecting both crew and high-value equipment.
Security: Ensure mission and data integrity through an integrated Smart BMS, which filters interference and monitors health status to prevent operational failures.
Sustainability: Leverage ultra-long service lives to reduce environmental waste and optimize long-term fleet ROI.
Standardization: Establish uniform energy protocols across your fleet to ensure consistent performance in diverse UHV environments.
Simplicity: Reduce operational complexity with ultra-fast charging and plug-and-play integration for existing UAV models.
Scalability: Deploy power systems designed to grow with your fleet, supporting increased payload capacities and extended mission ranges.
Adopting this structured methodology ensures that every technical advantage of semi-solid technology is fully realized at an institutional scale.
Risk Mitigation through Industrial Reliability
In 500kV and 765kV+ environments, reliability is a baseline for mission success. Mitigating the risks inherent in high-voltage operations requires transitioning toward industrial-grade power solutions engineered for extreme stress.
Resilient Battery Performance: Semi-solid state technology provides superior physical resilience by utilizing a gel-like electrolyte. Even under intense electromagnetic stress, these batteries maintain a stable discharge curve, ensuring reliable performance for heavy-lift and long-range inspections.
Intelligent EMI Defense via Smart BMS: An integrated Smart BMS serves as a proactive defense layer. By actively filtering signal noise and monitoring real-time health (SoH), it prevents EMI from triggering false safety shutdowns, thereby enhancing communication stability and data integrity.
By leveraging these solutions, you can significantly reduce the operational risks associated with EMI and thermal stress, ensuring your fleet operates with the reliability required for critical infrastructure protection.
As the industry moves toward 24/7 unmanned grid operations, EMI resilience and power system integrity are the defining factors of mission success. Prioritizing these elements ensures your fleet remains mission-ready for the most demanding UHV environments.
Higher Accuracy: Reliable energy delivery ensures precise data collection for predictive maintenance and infrastructure audits.
Full Compliance: Standardized frameworks guarantee your operations meet stringent industrial safety standards.
Optimized ROI: High-cycle semi-solid technology (1,000–3,000 cycles) significantly lowers your Total Cost of Ownership.
To help navigate the technical complexities of EMI and power reliability, we invite you to consult with our engineering specialists for a Fleet Power Compliance Audit tailored to your grid inspection requirements.
FAQ
What is EMI, and why is it a concern for drone inspections?
EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) disrupts drone telemetry and GPS sensors. In 500kV+ environments, this can cause positioning drift or signal loss, leading to mission failure or asset damage.
How can shielding improve drone performance?
Effective shielding maintains a stable current and filters electrical noise. This ensures that onboard sensors capture the high-precision data required for infrastructure health assessments and regulatory audits.
What role does the Herewin Smart BMS play in EMI mitigation?
An integrated Smart BMS acts as a proactive defense layer. It filters electrical interference and provides real-time health detection (SoH), preventing “false safety shutdowns” and ensuring stable communication in high-stress zones.
How do semi-solid state batteries enhance drone safety?
By reducing liquid content to 5%-10%, these batteries lower temperature rise rates by 60% during extreme scenarios. This chemistry inherently minimizes the risk of thermal runaway and leakage.
Why is regulatory compliance important in drone inspections?
With energy densities of 300-400 Wh/kg and a life of 1,000–3,000 cycles, these batteries significantly reduce operational costs. When combined with verifiable BMS data, they ensure full alignment with industrial safety standards and audit-ready reporting.
See Also
Enhancing Drone Flight Time With High Energy Density Batteries
Ensuring Safe Charging Practices For High-Voltage Drone Batteries
The Importance Of Advanced Batteries For Safe Drone Logistics
Transforming Drone Safety With Smart BMS And Endurance Batteries