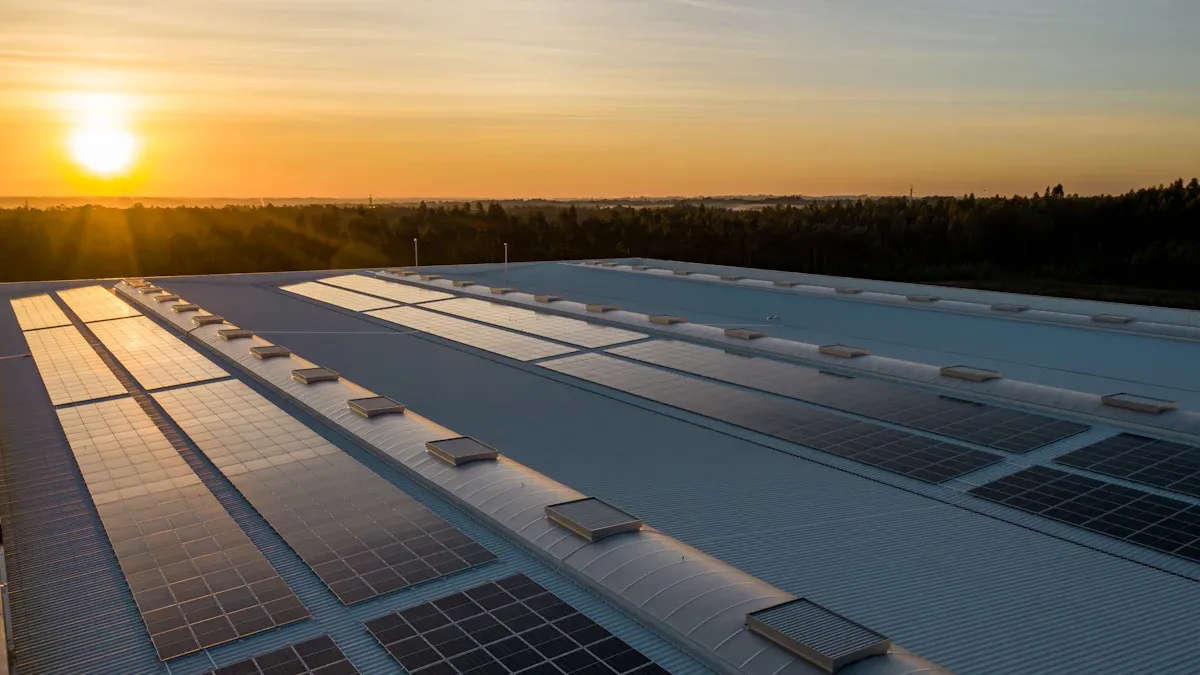
Homes are transforming their energy consumption patterns, driven by a growing demand for resilient and sustainable power solutions. The home solar energy storage market is experiencing significant expansion, projected to reach approximately $292.1 billion by 2034, a substantial increase from the 2024 baseline of $51.3 billion. Market momentum has accelerated dramatically: recent data shows that the percentage of new residential solar installations bundled with batteries has more than doubled since 2023, with adoption rates now routinely exceeding 34% nationwide. For large-scale development projects, Residential Solar Storage Integration is becoming essential, moving beyond mere solar panel installations. This integration effectively addresses power grid challenges, enhances property value, and meets evolving consumer preferences.
주요 내용
Home solar storage adds value to houses. It helps with the need for steady power.
Builders can use tax breaks and state help. These make solar storage projects earn more money.
Picking the best tech and helpers matters. This makes sure systems work well and last.
Knowing costs and dangers helps builders. It makes sure solar storage projects make good money.
Strategic Imperatives & Market Value
Enhancing Grid Stability and Resilience
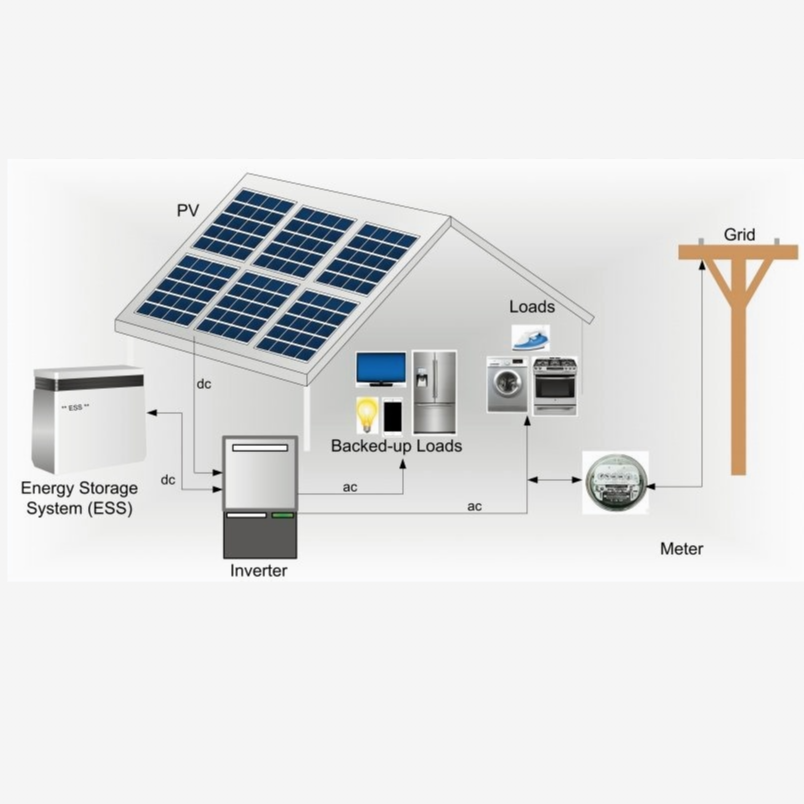
Residential solar storage makes the grid much steadier. It gives important backup power when the electricity goes out. Tools like NREL’s REopt Lite measure these good points. They find the best system sizes. They also show how long critical things can run. The CSE’s SERA tool figures out money saved by keeping power on. This shows how much stronger the system is. A solar system of 7–10 kW with a 20–40 kWh battery usually gives 24 hours of backup. Many homes using solar storage help a lot. They make power outages shorter. They also lower pollution.
Maximizing Incentives and Rebates
Developers can leverage multiple federal and state incentives to significantly enhance project economics and Return on Investment (ROI).
Federal Incentives (Extended under the Inflation Reduction Act – IRA):
Investment Tax Credit (ITC) – Section 48: Applies to commercially-owned PV and storage systems. The 30% base credit has been extended through 2032 before beginning a phase-down. Storage systems (battery capacity 3kWh) qualify whether installed with solar or as standalone units.
Residential Clean Energy Tax Credit – Section 25D: Applicable to systems purchased and installed by homeowners. The 30% credit is also extended through 2032 under the IRA. Systems must be placed in service before December 31, 2032.
Note:The IRA substantially extended the term of these key credits. Project developers should carefully study the adders (e.g., domestic content, energy community deployment) to qualify for increased credit amounts, potentially reaching 40-50%.
State and Local Programs:
Direct Cash Rebates/Incentives: Such as California’s Self-Generation Incentive Program (SGIP), which provides performance-based cash incentives for storage, with a focus on high-risk (resilience) areas.
Performance-Based Incentives: Like the Massachusetts SMART Program, offering long-term revenue streams tied to grid services.
Other Initiatives: Including the New York NY-Sun Program, which provides capacity-based incentives and supports the integration of community solar and storage.
Increasing Property Value and Market Appeal
Adding residential solar storage makes homes worth more. It also makes new homes more attractive. Better battery tech makes homes more independent. This is good where power often goes out. Market data shows a significant surge in property listings mentioning battery storage, reflecting the strong consumer demand for energy resilience. Solar and battery parts are cheaper. Electricity rates are going up. People want stronger power. All these things help. Homes with solar and storage sell for more. This helps builders make their projects stand out.
Meeting Evolving Consumer Demands
People want residential solar storage more and more. They want protection from power grid problems. This is clear from planned power shut-offs. Saving money is another reason. Changes in net metering make storing energy better. People want more freedom and control. They want energy independence and to save money. Homeowners want to rely less on the grid. They want to lower high electricity bills. Making solar work best is important. Storing extra energy for night use is key. More than 80% of home battery owners want backup power most. They say it helps during blackouts.
Technology & Integration Strategy

Technology Selection and System Sizing
Developers must select the appropriate technology and size systems based on project goals (i.e., backup power, solar self-consumption, or peak shaving/arbitrage). System sizing begins with a detailed baseline load analysis to determine the energy needs of critical loads (e.g., refrigerator 1600 Wh, Wi-Fi 240 Wh, totaling 2.4 kWh). Design must factor in key metrics like Capacity (kWh), Power Rating (kW), and a high Depth of Discharge (DoD).
Deeper technical considerations include:
Topology: Balancing between the high-efficiency, complex DC-Coupled system and the simpler, slightly lower-efficiency AC-Coupled system.
Battery Chemistry: Prioritizing safe, long-cycle-life Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4), while monitoring emerging technologies.
System Efficiency: Modeling must ensure the holistic round-trip efficiency reaches or exceeds 85%.
Accurate system sizing and smart technology choices are fundamental to realizing the projected ROI, ensuring the system meets performance guarantees across its full lifespan.
System Reliability & Partnering
Long-term reliability and life-cycle cost are paramount. To ensure the system performs over its expected lifetime, developers must establish strategic partnerships with verified, technologically advanced suppliers. Key supplier selection criteria should be rigorously evaluated:
Technology and Safety: Prioritize safer, longer-cycle-life chemistries like Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) and require strict certification to international standards (e.g., UL 9540).
Performance: Scrutinize metrics such as deep cycle capability, ensuring the system offers 4,000 to 6,000 cycles or more.
Warranty: Review rigorous terms, including the 10-year or 7,300-cycle limit and guaranteed end-of-life capacity.
Supply Chain & Deployment Assurance: Partner with major suppliers known for stable supply capacity and high-quality standards to mitigate material and logistics risks.
Herewin, a provider of residential Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) storage, offers modular systems typically achieving 4,000 to 6,000 cycles. Developers are encouraged to use such cycle life and modularity metrics as core criteria when evaluating any solution.
Regulatory Landscape and State Policy Frameworks
Battery storage rules are complex. A significant challenge stems from the lack of a unified definition for battery storage; it can function as generation, transmission, load, or demand response. This functional versatility means it does not fit neatly into one regulatory category. The specific regulatory authority is determined by the nature of the transaction. FERC oversees battery storage related to interstate power sales or wholesale transactions, while state regulations primarily apply when batteries generate power. FERC maintains jurisdiction even over local battery storage if it participates in the wholesale or retail power markets. Clear regulations are essential, as they demonstrate the value of battery storage, support developers and lenders, while poor regulations can stifle investment. Behind-the-meter home batteries provide grid support by reducing customer consumption during peak periods. Financial incentives, such as Time-of-Use programs, encourage saving power when costs are low and using it when costs are high.
Interconnection Requirements and Utility Relations
Developers must follow connection rules. They need good utility ties. Each utility has its own rules. These are for connecting solar and storage. Rules cover safety. They cover technical standards. They cover how to apply. Talk to utilities early. This helps get approvals fast. It avoids delays. Know local utility rules. Like net metering. Or time-of-use rates. This is important. It makes sure systems work best. It helps homeowners and the grid. Clear talks and following rules are key. This helps projects succeed.
Investment Modeling and Long-Term ROI
Calculating Return on Investment (ROI)
Project developers must figure out the Return on Investment (ROI). This is for residential solar storage projects. It shows how much money they will make. ROI looks at money saved on energy. It also counts special offers. It includes higher property value. Developers check how much homeowners save. This is on electricity bills. They also add state and federal money back. These savings help make a good ROI. A higher ROI makes projects look better. This is for investors and buyers.
Understanding Capital Expenditure (CapEx) and Operational Expenditure (OpEx)
Developers need a clear understanding of both CapEx and OpEx. CapEx covers all initial costs, where hardware components (modules, inverters, storage) typically constitute half to 60% of the total cost, depending on system size. Remaining CapEx includes Soft Costs like permits, net metering applications, and fire regulations, which vary significantly by location.
OpEx covers costs that keep happening and is critical for long-term ROI assessment. Beyond routine maintenance and potential battery replacements, enterprise developers must account for:
Remote O&M & Data: Licensing fees for professional Energy Management Systems (EMS) and monitoring platforms, plus associated data transmission and cloud hosting costs.
Cybersecurity: Investment in system security protocols and continuous firmware updates to mitigate risks to connected DERs (Distributed Energy Resources).
Insurance & Compliance: Ongoing premiums and costs related to system compliance and regulatory reporting.
A strong Operations and Maintenance (O&M) plan is vital to ensure long-term performance and rapid issue resolution.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation Strategies
Residential solar storage projects face financial and operational risks that developers must identify and manage.
Main Financial and Market Risks:
Default Risk: Risk of homeowner loan default, often related to personal finances or insufficient energy savings realization.
Market Risk: Changes in the solar market landscape, including new competing technologies or shifts in government policy.
Interest Rate Risk: Changes in lending program interest rates that can negatively impact project profitability.
Regulatory Risk: Changes in laws or energy regulations (e.g., shifts in tax credits or net metering rules).
Main Technical and Operational Risks:
Technology Risk: System components (PV panels, batteries, inverters) may underperform, leading to lower energy savings than projected.
Warranty Risk: The failure to ensure that adding storage does not void existing guarantees on power generation equipment.
Mitigation Strategies:
Developers should employ robust strategies to reduce technological and market risks. This includes diversifying energy generation sources (e.g., mixing solar with storage) and utilizing established market rules to minimize regulatory change impacts.
For project integrity, developers must:
Maintain ITC Compliance: Ensure that no more than 25% of stored energy originates from non-solar or non-wind sources to avoid partial loss of the Investment Tax Credit (ITC).
Scrutinize Warranties: Verify that adding storage does not cancel existing guarantees from power generation component manufacturers.
Engage Regulators: Seek clear guidance from regulatory bodies to ensure storage contracts and deployment methods comply with evolving policy frameworks.
Plan for Longevity: Design systems that account for battery limitations (charge rates, thermal needs, cycle limits) and include planned battery replacements for long-term power purchase agreements (PPAs).
Accessing Financing and Funding Opportunities
Developers have many ways to get money. This is for Residential Solar Storage Integration projects. These ways help make projects work.
Top money options include:
Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs): A company owns the PV system. The customer buys power at a set price. This is for a long time. It is usually 10-25 years. PPAs are liked by customers. These customers have low or no tax to pay. The owner gets tax benefits. This is like the 30% Federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC). They also get depreciation. These savings go to the customer. PPAs can start with no money down. They may also have price increases. This is for first savings.
Solar Leases: These are like PPAs. A company owns the PV system. The customer leases it. The owner gets tax benefits. These benefits can go to the customer.
Energy Services Agreements: This is another money option. A company gives energy services.
Tax Equity Financing Structures: These include selling and leasing back. They also include partnership flips. They let investors use tax benefits.
Cash or Loan Purchases: Customers can buy the system. They can use cash or a loan.
Supply Chain & Deployment Assurance
A robust supply chain strategy is essential for mitigating project delays, managing cost volatility, and ensuring quality assurance during deployment. Developers should mitigate risks associated with global disruptions by implementing diversified sourcing, utilizing multiple suppliers and contract manufacturers. Effective inventory management and logistics planning are necessary to prevent material shortages while minimizing carrying costs. Furthermore, developers should prioritize localization by sourcing components and Balance of System (BoS) hardware regionally when feasible to reduce shipping times and logistics costs. For Quality Assurance, it is critical to work only with primary suppliers who demonstrate compliance with global safety standards and offer full traceability of materials, ensuring consistent product quality across all development projects.
Residential solar storage is no longer optional—it is a strategic imperative that enhances property value, improves grid resilience, and meets evolving consumer demands. With the market projected for substantial growth, project developers must leverage these incentives and integration strategies now to secure a leadership position in the future energy landscape.
Ready to integrate? For specialized technical consultation and project solutions, contact the Herewin expert team today.
자주 묻는 질문
What is the main good thing about home solar storage for builders?
Builders make homes worth more. They make homes more wanted. People want power on their own. They want strong power. This also makes the power grid steady. It helps get the most money back.
What battery type does Herewin suggest for home power storage?
Herewin suggests good LiFePO4 batteries. These batteries are very safe. They last a long time. They save money. They work for 4,000 to 6,000 times. Their parts fit together easily. They work with solar and grid power.
How do builders make sure systems last a long time?
Builders work with good suppliers. Herewin is one. They pick good parts. LiFePO4 batteries last long. Good plans for upkeep help. Full guarantees also make systems work well.
What money help is there for home solar storage projects?
Builders can use the 30% federal tax credit. State programs also give money back. California’s SGIP is one. New York’s NY-Sun is another. These help projects make more money.
참고 항목
GWh Storage: Financial and Regulatory Strategies for Semi-Solid Energy Systems
Optimizing RV Lithium Battery Capacity: A Strategic Guide for 200Ah to 600Ah
Unlocking Energy Storage Opportunities for Turkey’s Renewable Transition
Boosting EV Safety and Supply Chain Resilience with Semi-Solid Batteries