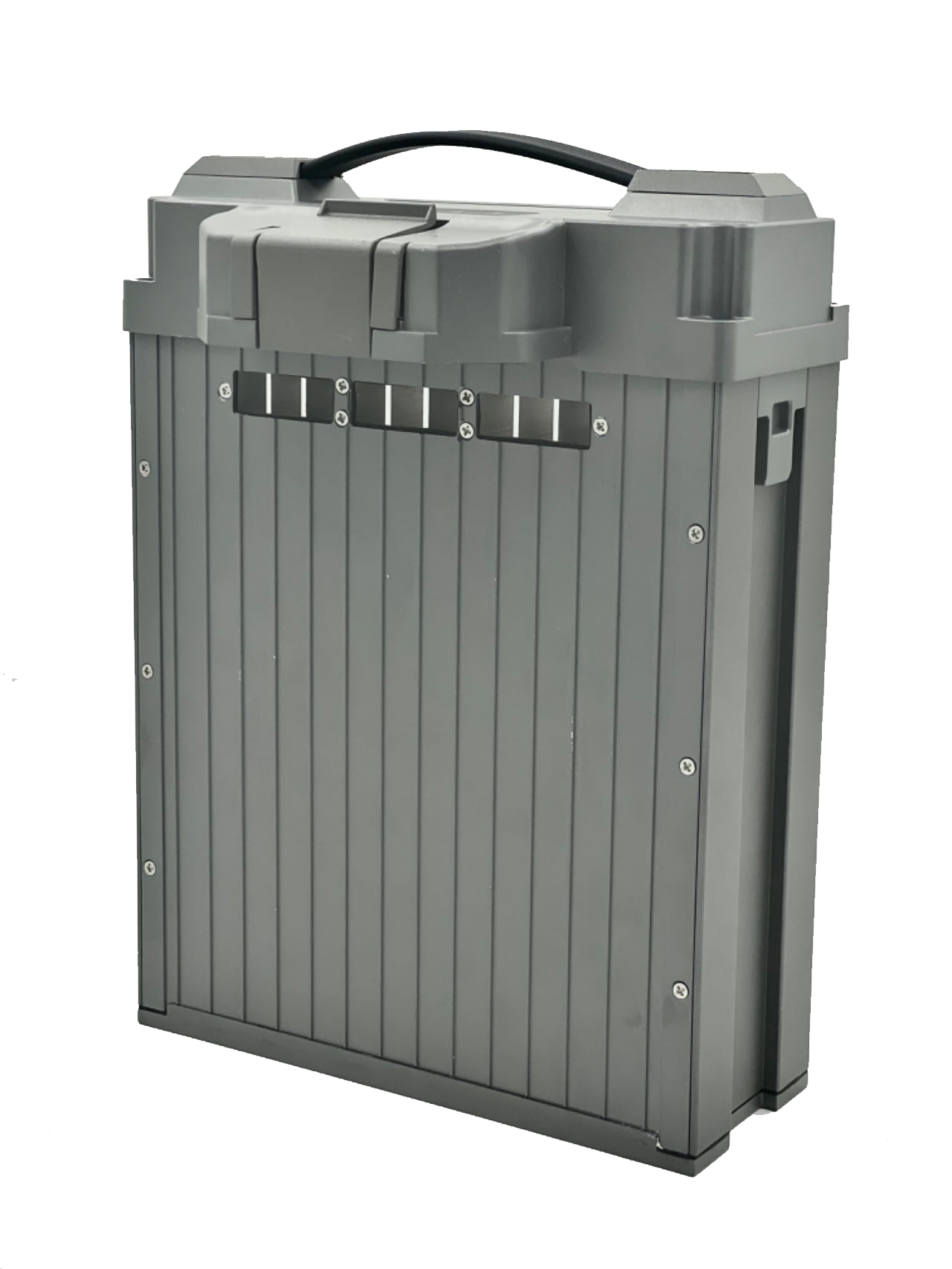
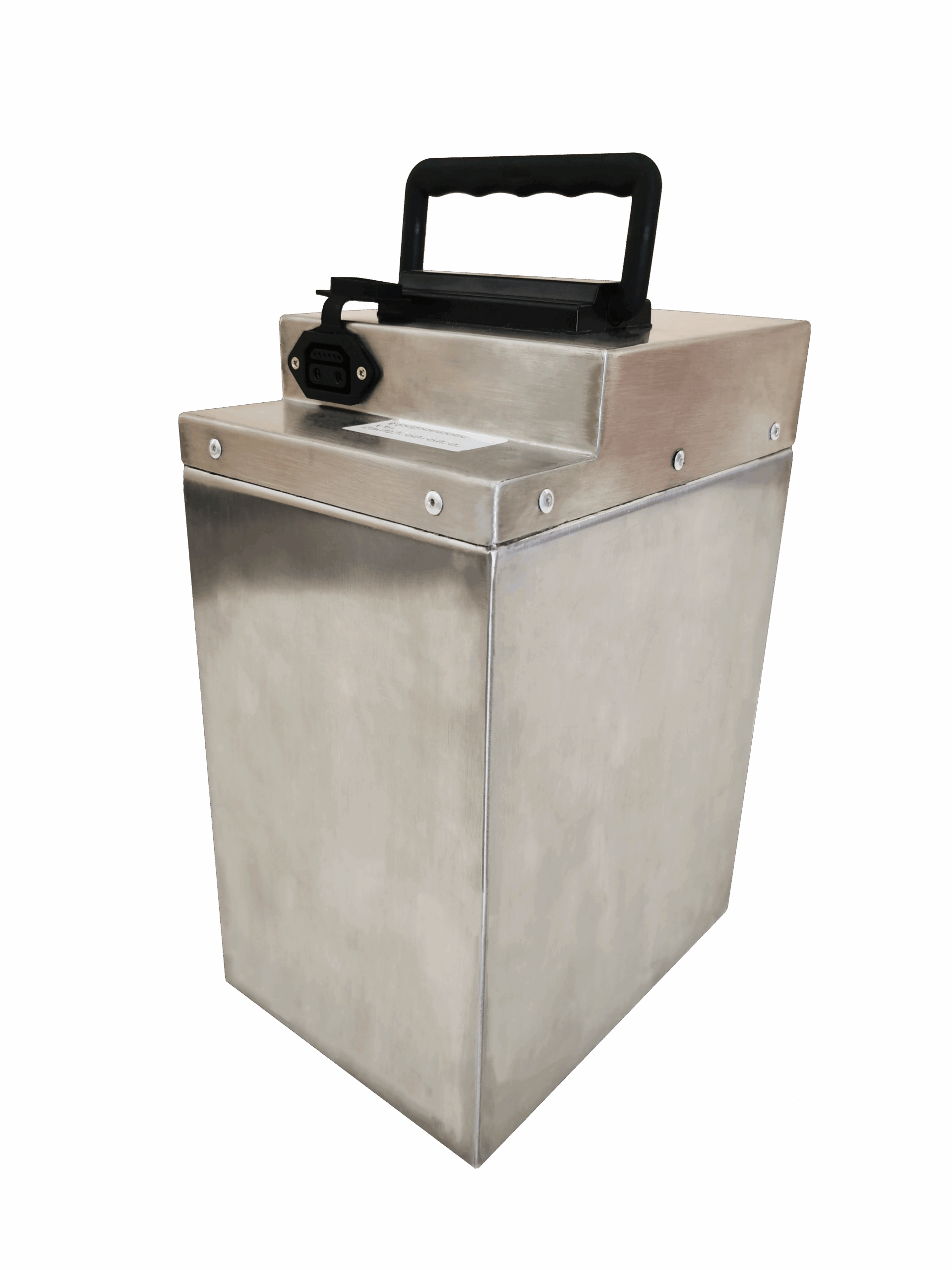
In the high-density Battery Energy Storage System (BESS) market, enclosure material selection is no longer just a physical requirement—it is a critical driver of asset longevity and thermal stability. For rack-mounted LFP systems, the housing acts as a primary barrier against thermal runaway and environmental degradation. Choosing between Aluminum, Steel, or Composites directly impacts whether your cells maintain a strict ΔT ≤ 3 ℃ temperature differential or face accelerated failure. This guide provides an engineering-grade analysis to help you balance structural integrity with an optimized Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
Основные выводы
Thermal Leadership: Aluminum’s high thermal conductivity (160W/(m·K)) is essential for high-density indoor integration, extending cell life up to 18 years.
Structural Containment: Steel offers a 1538℃melting point and 1000MPa yield strength, providing superior fire and impact barriers for utility-scale outdoor projects.
Electrical Isolation: Advanced composites deliver >50GΩ insulation resistance and UV aging retention (>80%), ideal for specialized or harsh chemical environments.
Precision Manufacturing: All rack-mounted solutions must adhere to a ±0.5mm tolerance to ensure seamless 19-inch standardized integration.
Decision Framework: A structured 5-step checklist—from Scenario Audit to TCO Audit—is vital for risk mitigation in BESS asset protection.
The Strategic Value of Housing Material
Material Comparison TL;DR Table
When evaluating materials for LFP battery housing, decisions must be driven by quantifiable engineering metrics. The following table compares the critical performance benchmarks and strategic TCO attributes of each option:
Material | Density | Thermal Conductivity | Melting Point | Key Advantage | TCO Attribute |
Aluminum | 2.7 g/cm3 | 160 W/(m.K) | 660 Celsius | Passive Cooling | Optimal OPEX |
Steel | 7.8 g/cm3 | 50 W/(m.K) | 1538 Celsius | Fire Containment | Low CAPEX |
Composites | 1.8 g/cm3 | 0.3 W/(m.K) | Charring (FV0) | Electrical Isolation | Specialized |
Aluminum: Strategically selected for high-density indoor environments like data centers. Its 160 W/(m.K) conductivity is the primary driver for maintaining a temperature differential (delta T) of 3 degrees Celsius or less, which is critical for extending cell service life to 18 years.
Steel: The benchmark for outdoor utility-scale BESS where structural containment and fire safety are non-negotiable. With a 1538 Celsius melting point and 1000MPa yield strength, it serves as the ultimate barrier against external impacts and internal thermal runaway risks.
Composites: Engineered for specialized high-voltage or corrosive scenarios. Beyond being 33 percent lighter than aluminum, they provide a critical insulation barrier of more than 50G.ohm and remain resilient against electrolyte leakage and UV aging.
Understanding these materials’ strategic value is essential for effective material selection in your LFP battery housing. By choosing the right material, you enhance the safety, durability, and overall performance of your energy storage solutions.
Core Materials: Performance vs. Application
Aluminum: Thermal Efficiency & Lightweighting
Aluminum has established itself as the engineering benchmark for heat management in high-density LFP storage systems. Unlike standard materials, the specialized 6061-T6 series alloys used in these enclosures provide a high thermal conductivity of 160 W/(m.K), which serves as a primary defense against cell degradation.
In practical application, this superior thermal profile allows for a 5 to 8 degrees Celsius reduction in internal pack temperatures, while maintaining a consistent temperature differential (delta T) of 3 degrees Celsius or less across the entire rack. This dual efficiency ensures the precise thermal environment required to extend the service life of LFP cells to a remarkable 18 years.
Beyond thermal performance, aluminum offers significant advantages in structural integration. Its low density of 2.7 g/cm3 facilitates rapid deployment in multi-layer rack configurations, ensuring that systems stay well within floor load limits for data centers and UPS rooms. Furthermore, the use of high-precision extrusion techniques ensures a manufacturing tolerance of plus or minus 0.5mm, enabling seamless compatibility with standardized 19-inch rack infrastructures.
While steel remains superior in extreme impact scenarios or high-temperature fire containment (due to its higher melting point), aluminum’s balance of precision, lightweighting, and passive cooling makes it the optimal strategic choice for indoor energy storage assets where operational efficiency and longevity are the highest priorities.
Steel: Fire Containment & Structural Strength
Steel remains the industry standard for utility-scale outdoor BESS where structural safety and fire containment are the non-negotiable priorities. Unlike lighter alternatives, the high-grade steel used in energy storage enclosures offers a superior yield strength of 1000 MPa, providing an exceptional physical barrier against mechanical stress, external impacts, and seismic vibrations common in large-scale grid installations.
The most critical advantage of steel in a BESS environment is its extreme thermal resilience. With a melting point of 1538 degrees Celsius, steel provides a robust fire containment shield that remains structurally sound even during a severe thermal runaway event. This safety profile is essential for meeting stringent global standards like UL 9540A, ensuring that any internal fire is localized and prevented from spreading to adjacent battery modules or surrounding infrastructure.
However, the strategic use of steel requires a balanced consideration of its physical properties. Its high density of 7.8 g/cm3 contributes to higher transportation costs and requires reinforced foundation planning for outdoor sites. Furthermore, while steel is naturally susceptible to oxidation, modern BESS enclosures mitigate this through specialized anti-corrosion treatments, such as fluorocarbon coatings. These coatings enable steel housings to pass rigorous 2000-hour neutral salt spray tests, making them a reliable long-term investment for coastal or high-humidity outdoor environments where low initial capital expenditure (CAPEX) is a key project driver.
Composites: Insulation & Chemical Resistance
Composite materials, specifically high-performance fiberglass-reinforced polymers, represent a specialized category for BESS environments where electrical isolation and chemical stability are the primary engineering goals. With a low thermal conductivity of 0.3 W/(m.K), these materials act as highly effective thermal barriers, preventing the rapid transfer of heat between battery modules and enhancing the overall fire safety of the rack system.
The standout technical advantage of composites is their exceptional dielectric strength. They deliver an insulation resistance of more than 50G.ohm, providing a critical safety margin for high-voltage systems where electrical leakage must be eliminated. Furthermore, their resilience in aggressive environments is unmatched; they are immune to electrolyte corrosion and can maintain over 80 percent of their mechanical properties even after 1000 hours of intensive UV aging exposure.
While offering these high-end protection features, composites require a strategic approach to project budgeting due to their higher initial cost compared to aluminum or steel. Their extremely lightweight nature—being 33 percent lighter than aluminum—can offset some of these costs by reducing shipping and installation labor. However, in heavy-duty or high-vibration industrial settings, engineers must carefully evaluate their structural design, as composites can exhibit more brittleness than ductile metals under extreme mechanical fatigue.
Safety: Thermal Runaway & Corrosion Defense
Fire Strategy: Managing LFP Thermal Runaway
While Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) is inherently more stable than other lithium-ion chemistries, effective fire strategy remains the cornerstone of BESS safety. Managing the risk of thermal runaway—typically triggered by factors such as overcharging, manufacturing defects, or external overheating—requires a housing material that can maintain structural integrity when internal cell temperatures spike between 270 and 300 degrees Celsius.
To effectively mitigate these risks, a multi-layered defense strategy is essential:
Active Monitoring: Implementing advanced Battery Management Systems (BMS) to provide real-time tracking of charge levels and temperature fluctuations.
Thermal Barrier Integration: Utilizing housing materials with high thermal resistance, such as composites with a Limited Oxygen Index (LOI) of ≥28 percent, or steel with its 1538 degrees Celsius melting point to prevent fire propagation between racks.
Venting and Insulation: Incorporating intumescent polymers and robust separators that can withstand high-temperature exposure while facilitating controlled gas venting.
Precision Electrical Isolation: Ensuring high-voltage components are encased in materials providing more than 50G.ohm of insulation resistance to eliminate the risk of accidental short-circuiting.
By selecting housing materials that prioritize these thermal and electrical barriers, engineers can ensure that a single-cell failure does not escalate into a catastrophic system-wide event, thereby safeguarding both the asset and the surrounding facility.
Resilience: Salt Spray & UV Durability
Corrosion resistance is a vital safety consideration, particularly for BESS assets deployed in coastal or high-humidity regions. To ensure long-term reliability, housing materials must demonstrate resilience against aggressive environmental stressors. Aluminum and high-grade composites naturally excel in these conditions. Specifically, these materials are engineered to pass a 2000-hour neutral salt spray test, a benchmark that guarantees structural integrity in saline-rich atmospheres.
Furthermore, for systems exposed to direct sunlight, UV stability is non-negotiable. Our advanced composite housings are designed to maintain over 80 percent of their mechanical properties after 1000 hours of intensive UV aging exposure, preventing the brittleness and surface degradation that compromise safety over time. While steel is inherently more susceptible to oxidation, the application of specialized fluorocarbon coatings allows it to meet these same rigorous durability standards, providing a cost-effective solution for outdoor utility-scale installations.
Precision: 19-Inch Rack Integration
In the world of rack-mounted BESS, precision is not just a manufacturing preference—it is a requirement for operational stability. When integrating LFP battery modules into standardized 19-inch racks, even minor misalignments can lead to improper heat venting or mechanical stress on electrical connectors.
To address this, our engineering process maintains a strict manufacturing tolerance of plus or minus 0.5mm. This high-precision control ensures that every module fits perfectly within the rack, facilitating optimal airflow and secure mounting. By prioritizing these exact dimensions, Herewinpower delivers solutions that meet the most stringent safety standards while significantly enhancing the overall longevity and serviceability of your energy storage infrastructure.
Logic: 5-Step Engineering Checklist
From Scenario Audit to TCO Analysis
Selecting the optimal material for your LFP battery housing requires a systematic approach that balances immediate physical needs with long-term asset performance. Use this 5-step engineering checklist to ensure your BESS meets the highest industry standards for safety and efficiency.
1. Scenario Audit (Indoor vs. Outdoor)
Evaluate the primary stressors of your installation site. High-density indoor environments, such as Tier III data centers, demand the passive cooling efficiency of aluminum to maintain a cell temperature differential (delta T) of 3 degrees Celsius or less. In contrast, outdoor or utility-scale sites prioritize the 1538 degrees Celsius melting point of steel or the chemical immunity of composites to withstand extreme weather and potential fire propagation.
2. Metric Screening (Density/LOI)
Screen candidate materials against quantifiable safety and weight metrics. Focus on the Limited Oxygen Index (LOI) and density. For high-voltage or fire-sensitive applications, prioritize materials with an LOI of ≥ 28 percent (typically found in advanced composites) to ensure self-extinguishing properties. Simultaneously, verify that the material density—ranging from 1.8 g/cm3 (composites) to 7.8 g/cm3 (steel)—aligns with the floor loading capacity of your facility.
3. Candidate Matching
Align material properties with the strategic goals of your project. Beyond basic fit, consider the following technical pillars:
Thermal Reliability: Can the material maintain the operating environment required to maximize battery service life and performance.
Environmental Resistance: Does the housing meet the 2000-hour salt spray and 1000-hour UV aging standards.
Structural Integrity: Is the yield strength sufficient (e.g., 1000 MPa for steel) to handle the mechanical load of grid-scale energy throughput.
4. Integration Check (≤ 80% rack load)
Verify the compatibility of your selected material with standardized 19-inch rack systems. Ensure that the total weight of the housing and battery modules does not exceed 80 percent of the rack’s rated load capacity. Furthermore, insist on a manufacturing tolerance of plus or minus 0.5mm to prevent mechanical stress during installation and to ensure proper airflow for heat dissipation.
5. TCO Audit (Maintenance vs. CAPEX)
Finalize your selection through a Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) audit. While steel may offer a lower initial Capital Expenditure (CAPEX), the superior thermal management of aluminum can significantly reduce Operational Expenditure (OPEX) by lowering HVAC cooling costs and extending the asset’s cycle life. Evaluate whether the specialized durability of composites provides better long-term value in corrosive environments despite their higher upfront cost.
Proven Results: BESS Case Studies
Data Center: ΔT ≤ 3°C Efficiency and TCO Optimization (10MWh)
Herewinpower successfully implemented a 10MWh 19-inch rack-mounted liquid-cooled LFP system for a Tier III data center . Facing a strict floor loading limit of 2.7t or less per cabinet, the project utilized precision-engineered 6061 aluminum housing to ensure a total cabinet weight of only 2.5t, perfectly matching the facility’s structural constraints .
Thermal Performance: The high-conductivity aluminum (160 W/(m.K)) limited cell temperature differentials to 3℃ Celsius or less .
Asset Impact: This superior thermal control reduced the annual capacity degradation rate to just 3.2% (compared to 8.1% in standard air-cooled alternatives), effectively extending the project’s service life to 18 years.
Cost Efficiency: The maintenance-free nature of the anodized aluminum housing reduced annual operational expenditure (OPEX) by 12,000 RMB per 10MWh compared to traditional steel-based solutions.
Coastal Site: Level 12+ Typhoon Defense and Corrosion Resilience (20MWh)
For a 20MWh utility-scale installation in a high-salinity coastal zone, Herewinpower delivered a BESS solution engineered for extreme environmental resilience and a 20-year operational lifespan .
Structural Integrity: Utilizing high-strength 316L stainless steel with a yield strength of 1000 MPa, the housing successfully met the mechanical requirements for Level 12+ typhoon defense and impact resistance .
Advanced Coating: The enclosures were treated with specialized fluorocarbon coatings, successfully passing a 2000-hour neutral salt spray test without signs of corrosion .
Safety and Maintenance: The system demonstrated superior fire safety by maintaining structural integrity for over 5 minutes under high-temperature flames, passing UL 9540A standards . Annual maintenance costs were optimized at 8,000 RMB per 20MWh, saving 5,000 RMB annually compared to standard aluminum options in harsh marine environments.
Selecting the optimal housing material is a strategic investment in the safety and longevity of your energy storage assets. By balancing scenario adaptation with technical performance—such as maintaining a ΔT ≤ 3°C to achieve an 18-year battery service life —you ensure a reliable system that optimizes the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
To make informed decisions for your next BESS project, consider consulting with our engineering team for a custom technical assessment to determine the best material fit for your specific environment.
ЧАСТО ЗАДАВАЕМЫЕ ВОПРОСЫ
What is LFP battery technology?
LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) is a high-safety battery chemistry known for thermal stability. When integrated with professional housing, it can offer an asset service life of up to 18 years and endure 6,000 to 10,000 cycles.
Why choose aluminum for LFP battery housing?
Aluminum is selected for high-density indoor sites due to its 160 W/(m.K) thermal conductivity. It maintains a temperature differential (delta T) of 3 degrees Celsius or less, which is critical for extending cell longevity.
How does steel compare to aluminum in battery housing?
Steel prioritizes structural safety with a 1538 degrees Celsius melting point and 1000 MPa yield strength. While heavier, it is the most cost-effective fire and impact barrier for outdoor utility-scale projects.
What are the benefits of using composites in LFP battery housing?
Composites are over 30 percent lighter than aluminum and provide superior electrical isolation with a resistance of more than 50G.ohm. They are ideal for corrosive or high-voltage environments where traditional metals may degrade.
How do I ensure safety in my LFP battery system?
Safety requires combining an advanced BMS with high-precision housing (maintaining a plus or minus 0.5mm tolerance). Using materials that pass 2000-hour salt spray tests ensures the structural integrity of the entire BESS enclosure over its lifecycle.
См. также
Ensuring Safety and Longevity with High-Temperature LFP Solutions
Essential Guide to RV System Compatibility for Lithium Upgrades
Comparative Performance Tests: Lead-Acid Versus Lithium Batteries in RVs